[et_pb_section bb_built=”1″][et_pb_row][et_pb_column type=”1_2″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
The design of organs for the development of medicine and technology is very important because it constitutes one of the most promising professions of the future.
One of the most important positive consequences is that it will eliminate waiting lists for transplants because organs can be designed as they avoid years of suffering and even death.
The challenge facing organ designers is to venture into the manufacture of structures from the cells of the person itself as a method of protection against the rejection that the body could generate towards a technology.
The myocardium (myo: muscle and cardio: heart), is the muscle tissue of the heart, muscle responsible for pumping blood through the circulatory system by contraction. The heart muscle works involuntarily, without having nerve stimulation, although this will not be able to regulate the heart rate.
Human beings are made up of cells, whose main structures are the membrane, the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Cells come together to form tissues, when they come together they form organs, which together constitute apparatuses and systems.
Epithelial tissue. The epithelial tissue is composed of tight sheets of cells that line the surfaces, including the outside of the body, and line the body cavities. For example, the outer layer of the skin is an epithelial tissue, as is the lining of the small intestine.
The human body consists of four basic types of tissues: conjunctive, epithelial, muscular and nervous. These sets of specialized cells perform such a diversity of functions that only the most advanced textbooks can include them all. The connective tissue is the most abundant of the four.
The tissues are those that form your organs (all of them) in such a way that each function that your organs perform is by the tissue or tissues that constitute it. To answer your question imagine any organ, think what it does and that is a function of a tissue (the one that constitutes this organ)
Colénquima. All the tissues fulfill a certain function so that the organism works in coordination and functions correctly the apparatus of which it is part and all the devices in turn are related so that the animal organism functions normally
A fabrication tool builds coronary tissue in 3D, which allows researchers to rapidly form complex biological tissue in a three-dimensional space.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][et_pb_column type=”1_2″][et_pb_text _builder_version=”3.13.1″]
Researchers have devised a semiautomated process to construct polymeric structures to guide the development of coronary tissue in three dimensions. The method, which involves a production by layers, will allow a more precise investigation of the three-dimensional indications that lead the cells to organize and form tissue; and could serve as a platform for the development of implantable organ tissue.
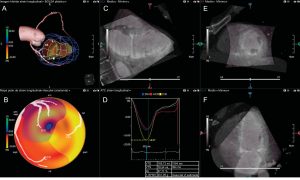
Tissue engineers can now make three-dimensional constructions of relatively simple fabrics. However, highly ordered cellular architectures are essential for the functioning of complex organs such as the heart that are much more difficult to replicate.
The tissue is grown in the laboratory by “seeding” structures, usually composed of an elastic or gelatinous porous material, with cells destined to become specific tissues. The function of cardiac tissue is due to its structure, in which individual cells align to form multicellular fibers, which in turn form sheets of tissue.
Recent work has focused on determining how to orient the cells so that they line up correctly and form these hierarchical components. However, this type of research has been limited, in its majority, to two dimensions. Kolewe and researcher Lisa Freed, from the Draper Laboratory, set out to develop a more precise way to control the design of the “networks” of pores, with the aim of adding a third dimension. A new work published in the journal Advanced Materials describes the research.
These and other innovations are also possible in Pharmamedic.
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]