Osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis is a slowly progressive chronic degenerative disease common in old age that affects the mobile joints of the body characterized by joint pain, marked tenderness, stiffness, impaired mobility, crepitus and effusion.
Arthrosis or osteoarthritis is generated from the cumulative damage from microscopic and macroscopic lesions in said joints that activate a maladaptive repair response that includes the activation of proinflammatory pathways of the innate immune system.
The disorder manifests first at the molecular and cellular level (abnormal metabolism of joint tissues) followed by anatomical or physiological changes (cartilage degradation and loss, bone remodeling, osteophyte formation, synovial inflammation, sclerosis, and thickening of subchondral bone). and loss of normal joint function). Hip and knee involvement are a common cause of disability.
Osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis is the most common rheumatic disease, especially among the elderly.
It occurs prematurely in people with genetic diseases that affect connective tissue, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and joint hypermobility syndrome.
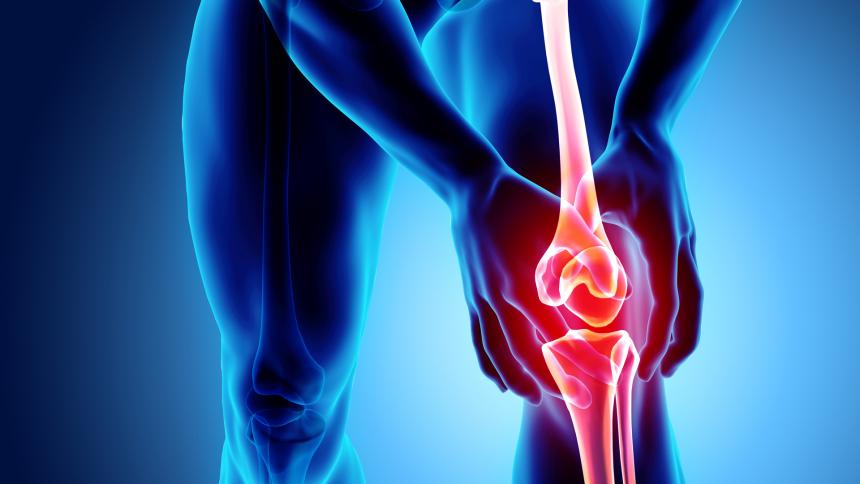
In osteoarthritis, the surface of the cartilage breaks down and wears away, causing the bones to move against each other, leading to friction, pain, swelling, and loss of motion in the joint. Over time, the joint may lose its original shape, and spurs may grow on it. In addition, pieces of bone and cartilage can break off and float within the joint space (joint mice), causing further pain and damage.
Osteoarthritis in the fingers seems to run in some families and not in others, so it is thought that it could be hereditary. It has been observed that it affects more women than men, especially after menopause. Small bone nodules may appear in the joints of the fingers. Heberden’s nodes, in the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands, or Bouchard’s nodes if they are in the proximal part. Fingers can become swollen, stiff, and twisted. The thumbs of the hands may also be affected (rhizarthrosis of the thumb).
The knees are the joints on which most of the body’s weight is carried (along with the ankles, but these move much less than the knees), so it exposes them to being most affected by osteoarthritis.
The prevalence of cervical-osteoarthritis and lumbar-osteoarthritis are more frequent in women and at an older age, as well as in people with low educational levels and obesity.
- Age: adults over 60 years of age.
- Sex: The same for both sexes, but in women it occurs at earlier ages (45 years).
- Women: Predominantly in the knees and in the interphalangeal joints (hands).
- Men: Predominates in the hip.
- Obesity: Quadruples the risk if the person is above the BMI considered normal.
There are three etiological types integrating primary osteoarthritis:
- Type I osteoarthritis, of genetic cause.
- Type II osteoarthritis, hormone dependent (postmenopausal).
- Type III osteoarthritis, related to age.
The objective of the treatments has focused on eradicating as much as possible the pain and other discomforts associated with this pathology through the administration of analgesics and anti-inflammatories.
https://www.msdmanuals.com/es/hogar/trastornos-de-los-huesos,-articulaciones-y-m%C3%BAsculos/enfermedadesarticulares/artrosis#:~:text=La%20artrosis%20es%20un%20trastorno,muy%20frecuente%20con%20el%20envejecimiento.https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artrosis